Infections With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Introduction:
Human immunodeficiency infection (HIV) could be a retrovirus. Retroviruses are encompassed RNA infections characterized by their component of replication by means of invert translation to deliver DNA duplicates that coordinated into the have cell’s genome.
There are 2 HIV sorts, HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 causes most HIV contaminations around the world, but HIV-2 causes a significant extent of contaminations in parts of West Africa. In a few ranges of West Africa, both infections are predominant and may coinfect patients. HIV-2 shows up to be less virulent than HIV-1. HIV-1 begun in Central Africa within the to begin with half of the 20th century, when a closely related chimpanzee infection to begin with contaminated people. Scourge worldwide spread started within the late 1970s, and Helps was recognized in 1981.

What is HIV?
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency infection. HIV contaminates and annihilates cells of your safe framework, making it difficult to battle off other infections. When HIV has seriously debilitated your safe framework, it can lead to obtained immunodeficiency disorder (AIDS).
Because HIV works in reverse to embed its informational into your DNA, it is called a retrovirus.
Where does HIV come from?
HIV contamination in people came from a sort of chimpanzee in Central Africa. Ponders appear that HIV may have hopped from chimpanzees to people as distant back as the late 1800s.
The chimpanzee form of the infection is called simian immunodeficiency infection. It was likely passed to people when people chased these chimpanzees for meat and came in contact with their contaminated blood.
Over decades, HIV gradually spread over Africa and afterward into other parts of the world. The infection has existed within the Joined together States since at slightest the mid to late 1970s.
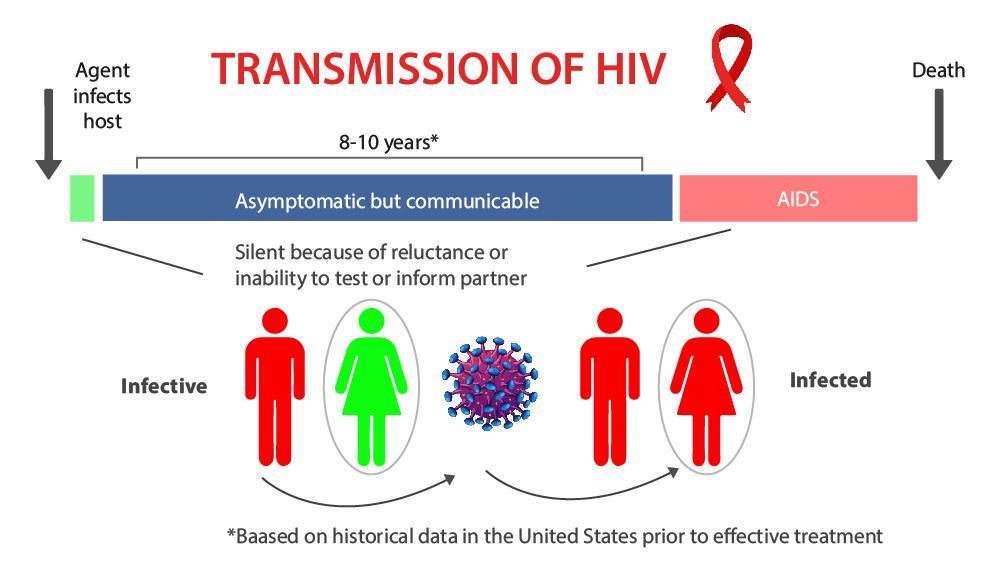
Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus requires contact with an open surface (such as a cut) uninfected individual with a body liquid that contains the infection or cells contaminated with the infection. HIV can show up in about any body liquid, but transmission happens basically through blood, semen, vaginal liquid, and breast drain. In spite of the fact that tears, pee, and spit may contain moo concentrations of HIV, transmission through these liquids is greatly uncommon, in the event that it happens at all.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus isn’t transmitted by contact that does not include trade of body liquids (such as touching, holding, or dry kissing) or by near, nonsexual contact (such as touching a surface or an question). No case of HIV transmission has been followed to the hacking or wheezing of an contaminated individual or to a mosquito nibble. Transmission from an tainted specialist or dental practitioner to a quiet is amazingly rare.
HIV is usually transmitted within the taking after ways:
- Sexual contact with an contaminated individual, when the mucous layer lining the mouth, vagina, penis, or rectum is uncovered to body liquids such as semen or vaginal liquids that contain HIV, as happens amid unprotected sexual intercourse
- Injection of sullied blood, as can happen when needles are shared or a wellbeing care laborer is inadvertently pricked with an HIV-contaminated needle
- Transfer from an tainted mother to a child some time recently birth, amid birth, or after birth through the mother’s milk
- Medical methods, such as transfusion of blood that contains Human Immunodeficiency Virus, strategies done with insufficiently sterilized disobedient, or transplantation of an contaminated organ or tissues
HIV is more likely to be transmitted on the off chance that skin or a mucous layer is torn or damaged—even on the off chance that negligibly. Amid vaginal or butt-centric sex, little cuts may happen within the private parts or encompassing skin, even if the individual isn’t mindful that a cut is present.
Most Human Immunodeficiency Virus contaminations are transmitted through hetero contact, but hazard variables shift concurring to locale. For occurrence, transmission among men who have sex with men is more often than not the foremost common way contamination happens in high-resource nations, but individuals who infuse drugs are disproportionally influenced in Southern Asia.
In regions where hetero transmission is overwhelming, Human Immunodeficiency Virus contamination takes after courses of exchange, transportation, and financial movement to cities and spreads optionally to country regions.
Through sexual activity
The risk of Human Immunodeficiency Virus is greatest during vaginal or anal sex when condoms are not used or used incorrectly. HIV transmission can also occur during oral sex, although the spread is less than during vaginal or anal sex.
The risk of HIV transmission increases if semen or vaginal fluids contain large amounts of Human Immunodeficiency Virus and/or tears or sores, even small, in the skin or membranes that cover the genitals, mouth or rectum. Therefore, infection is much more likely during the following times:
- In the first few weeks after infection, because this happens when the blood and body fluids have very high levels of HIV.
- Violent sexual activity that damages the skin or membranes. covering the genitals, mouth or rectum
- Sex if either partner has a genital herpes infection, syphilis or another sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause sores or tears in the skin or inflammation in the genitals
Human Immunodeficiency Virus medicines (antiretroviral medicines) can reduce the amount of HIV spread in semen and vaginal fluids. Therefore, treating HIV infection with these drugs can greatly reduce the chance of infection.
Sexual activities that can damage the membranes covering the genitals, mouth or rectum include fisting (inserting a hand or the whole hand into the anus or vagina) and using sex toys.
Research shows that people with HIV who are treated with antiretroviral therapy and have an undetectable viral load (virally suppressed) do not transmit the virus to their partners sexually.
With needles or other instruments
Healthcare workers who are accidentally injected with an HIV-infected needle have about a 1 in 300 chance of contracting HIV if they are not treated as soon as possible after exposure. Such treatment reduces the possibility of infection to less than 1:1500. The risk increases if the needle penetrates deeply, or if the needle is hollow and contains HIV-contaminated blood (such as a needle used to draw blood or inject drugs) rather than simply being covered in blood (such as a needle used for suturing).
Putting infected liquid into the mouth or eyes has less than a 1:1000 chance of infection.
From mother to baby
HIV infection in children has increased because more women are having children.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be transmitted from an HIV-infected mother to her children in the following ways:
- During pregnancy, through space the fetus
- During birth, to the baby as it passes through the birth canal
- After birth, to the baby through breast milk
Without antiretroviral therapy, the risk of mother-to-child transmission is as high as 45 percent.
Treating infected women with antiretroviral drugs greatly reduces the risk of transmission. Pregnant women infected with HIV should receive treatment during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, during delivery and during lactation. The risk is lower if you have a C-section and treat your baby a few weeks after birth.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be passed through breast milk. HIV-infected mothers should not breastfeed unless they live in an area where legal breastfeeding is safe and accessible. However, in areas where infectious diseases and malnutrition are common causes of child mortality and where safe and accessible child care is not available, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends breastfeeding and antiretroviral treatment for at least 12 months. In these situations, protection through breastfeeding against infection can eliminate the risk of HIV infection.
Because many women and their children are infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus, they receive treatment or take medication to prevent HIV infection. The number of children with AIDS is declining in many countries.
By blood transfusion or organ transplantation
Currently, only a small percentage of HIV is transmitted through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since 1985, in most rich countries, all blood transfusions have been tested. collected to reduce HIV and, as far as possible, part of the blood, products are heated. Risk of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Currently, the risk of contracting HIV from a single transfusion (tested for HIV or other blood-borne viruses) is less than 1 in 2 million in the United States. However, in many low-income countries, blood and blood products are not tested for HIV and have not been fully tested. There, the risk remains high.
HIV is transmitted when organs (kidney, liver, heart, pancreas, bone, skin) from infected donors are used incorrectly for transplants. Transplantation of tissues or certain tissues that have been treated (such as bone) can reduce the transmission of HIV.
Artificial Reproduction
Human Immunodeficiency Virus can also be transmitted during insemination using sperm from an infected donor. In the United States, steps have been taken to reduce this problem. Young seed samples are no longer used. Donor sperm will be kept frozen for at least six months. The donor is also tested for HIV before the sperm is used.
If the sperm donor is known to be infected with HIV, sperm purification is an effective way to remove HIV from the bread.
Symptoms of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
You can be infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus without symptoms. That’s why it’s important to get tested even if you’re not infected.
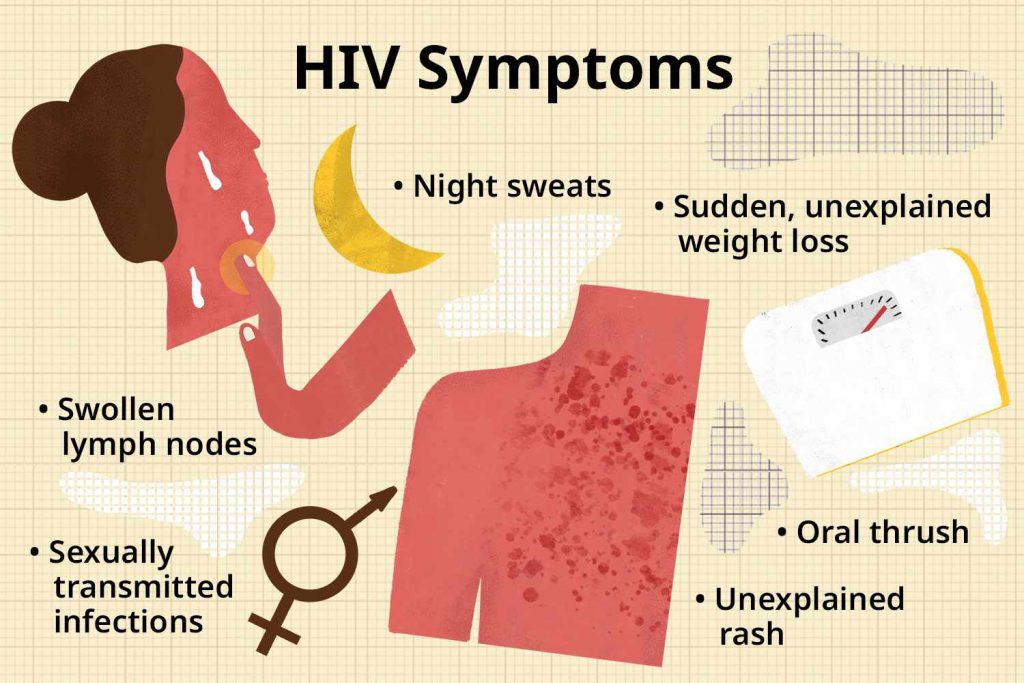
Sometimes when you’re infected with HIV, you may experience flu-like symptoms. These may include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Muscle pain
- Cold sweats
- Rash
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Swelling of the mouth
Stages Of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
stage no 1: Acute HIV
Some people develop flu symptoms a month or two after being infected with HIV. These symptoms usually go away within a week to a month.
stage no 2: Persistent stage/clinical inactivity
After the intense arrange, you’ll have Human Immunodeficiency Virus for numerous a long time without feeling sick. It’s vital to know that you just can still spread HIV to others indeed on the off chance that you are feeling well.
stage no 3: Aids
AIDS is the most serious form of HIV infection. At this point, HIV has severely weakened your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
Acquired infections are diseases that people with a healthy immune system can fight off. When HIV develops into AIDS, this disease contributes to a weakened immune system.
People with AIDS are more likely to develop cancer. These cancers and related diseases are called symptoms of AIDS.
To be diagnosed with AIDS, you must be infected with HIV and have one or more of the following:
- Have a CD4 count of less than 200. cubic millimeter of blood. (200 cells/mm3)
- AIDS is a defined disease
Causes of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
HIV can be found in the fluids of an infected person. This includes broth, sterile and diluted fluids, blood and breast milk.
This virus is a fragile virus and does not survive long outside the body. HIV cannot be transmitted through sweat, urine and saliva.
The most common way to get HIV in the UK is through vaginal or vaginal intercourse without a condom.
Other ways to get HIV are:
- Needles, syringes or other injections. Sharing equipment
- Transmission from mother to baby during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding
The risk of getting HIV through oral sex is very low, depending on many things, such as the way you work or your oral hygiene and oral hygiene of the person what you work with.
Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Antiretroviral treatment is recommended for all people infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. If left untreated, HIV can lead to serious complications, and newer, less toxic drugs have been developed. For most people, early treatment produces the best results. Studies have shown that people who are given antiretroviral drugs early are less likely to develop or die from AIDS-related complications.
Even if HIV levels are reduced to very low levels by There is no cure and treatment can maintain the virus at bay. outside the body, it cannot be removed. It can be found in blood, other body fluids or tissues. The goal of treatment is to:
- reduce HIV levels to undetectable levels
- restore CD4 counts to normal
Therefore, people must take pain medication for the rest of their lives.
Before starting treatment, people are instructed to:
- Take the medication as prescribed
- Do not skip doses
- Take medication for the rest of your life
It may be difficult to take medication as prescribed for the rest of your life. Some may skip a dose or stop taking medication for a short period of time (called a drug holiday). This practice is dangerous because HIV can develop drug resistance.
Because taking Human Immunodeficiency Virus drugs often leads to drug addiction, health care providers ensure that people are willing and able to follow their regimens. treatment to work To simplify medication regimens and help patients take their medications as prescribed, doctors often prescribe treatments that combine two or more medications into one pill to take just once a day.
Prevention of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
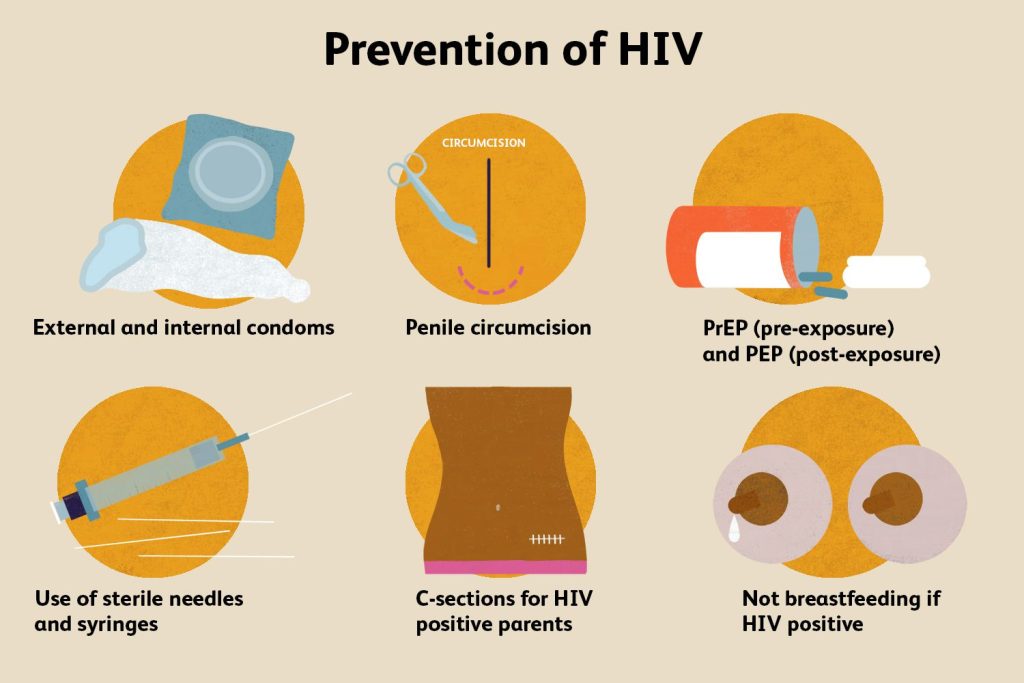
HIV may be a preventable disease. Reduce the chance of HIV contamination by:
- using a male or female condom amid sex
- being tried for HIV and sexually transmitted infections
- having a deliberate restorative male circumcision
- using hurt decrease administrations for individuals who infuse and utilize drugs.
Doctors may recommend solutions and therapeutic gadgets to assist avoid HIV, including:
- antiretroviral drugs (ARVs), counting verbal PrEP and long acting products
- dapivirine vaginal rings
- injectable long acting cabotegravir
- ARVs can moreover be utilized to anticipate moms from passing HIV to their children
People taking antiretroviral treatment (Craftsmanship) and who have no prove of infection within the blood will not pass HIV to their sexual accomplices. Get to to testing and Craftsmanship is an critical portion of avoiding HIV.
Conclusion:
Essential Human Immunodeficiency Virus contamination could be a basic period in which the virological and immunological occasions that take put, indeed some time recently the onset of clinical side effects, may decide the long-term result of malady. Early acknowledgment of indications, particularly in individuals considered to be high-risk people, is basic.
What are the infections associated with HIV?
HIV-related OIs include pneumonia, Salmonella infection, candidiasis, toxoplasmosis, and tuberculosis (TB). For people with HIV, the best protection against OIs is to take HIV medicines every day. HIV medicines prevent HIV from damaging the immune system.
What are HIV effects?
HIV Effects on the Immune System
Your body responds by making more CD4 cells, but after a while, it can’t keep up with the virus. This makes your immune system weak. You’re more likely to get sick, even from common germs. Infections last longer, are more severe, and might come back more often.